Findings (MAC III - Administrative Sensitive)
- Apache Web Server 2.4 Free
- Apache Web Server Versions
- Server Apache
- Apache Web Server 2.4.18
- Apache Web Server Download
New in httpd 2.4: If, ElseIf, and Else. Over the coming weeks, I'm going to be writing several articles about new features in Apache httpd 2.4. To me the most compelling reason to upgrade to Apache 2.4 today is the directive, so that's where I'll start. The Apache Software Foundation and the Apache HTTP Server Project are pleased to announce the release of version 2.4.46 of the Apache HTTP Server ('httpd'). This latest release from the 2.4.x stable branch represents the best available version of Apache HTTP Server. The Apache HTTP Server ('httpd') was launched in 1995 and it has been the most popular web server on the Internet since April 1996. It has celebrated its 25th birthday as a project in February 2020. The Apache HTTP Server is a project of The Apache Software Foundation. Apache httpd 2.4.46 Released 2020-08-07 ¶.
| Finding ID | Severity | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| V-214282 | Medium | The Apache web server must allow mappings to unused and vulnerable scripts to be removed. | Scripts allow server-side processing on behalf of the hosted application user or as processes needed in the implementation of hosted applications. Removing scripts not needed for application ... |
| V-214283 | Medium | The Apache web server must have resource mappings set to disable the serving of certain file types. | Resource mapping is the process of tying a particular file type to a process in the web server that can serve that type of file to a requesting client and to identify which file types are not to ... |
| V-214280 | Medium | The Apache web server must not perform user management for hosted applications. | User management and authentication can be an essential part of any application hosted by the web server. Along with authenticating users, the user management function must perform several other ... |
| V-214281 | Medium | The Apache web server must have Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) that invoke operating system shell programs disabled. | Controlling what a user of a hosted application can access is part of the security posture of the web server. Any time a user can access more functionality than is needed for the operation of the ... |
| V-214286 | Medium | The Apache web server must perform RFC 5280-compliant certification path validation. | A certificate's certification path is the path from the end entity certificate to a trusted root certification authority (CA). Certification path validation is necessary for a relying party to ... |
| V-214287 | Medium | Only authenticated system administrators or the designated PKI Sponsor for the Apache web server must have access to the Apache web servers private key. | The web server's private key is used to prove the identity of the server to clients and securely exchange the shared secret key used to encrypt communications between the web server and clients. ... |
| V-214284 | Medium | Users and scripts running on behalf of users must be contained to the document root or home directory tree of the Apache web server. | A web server is designed to deliver content and execute scripts or applications on the request of a client or user. Containing user requests to files in the directory tree of the hosted web ... |
| V-214285 | Medium | The Apache web server must be configured to use a specified IP address and port. | The web server must be configured to listen on a specified IP address and port. Without specifying an IP address and port for the web server to use, the web server will listen on all IP addresses ... |
| V-214288 | Medium | Cookies exchanged between the Apache web server and client, such as session cookies, must have security settings that disallow cookie access outside the originating Apache web server and hosted application. | Cookies are used to exchange data between the web server and the client. Cookies, such as a session cookie, may contain session information and user credentials used to maintain a persistent ... |
| V-214289 | Medium | The Apache web server must augment re-creation to a stable and known baseline. | Making certain that the web server has not been updated by an unauthorized user is always a concern. Adding patches, functions, and modules that are untested and not part of the baseline opens the ... |
| V-214303 | Medium | Cookies exchanged between the Apache web server and the client, such as session cookies, must have cookie properties set to force the encryption of cookies. | Cookies can be sent to a client using TLS/SSL to encrypt the cookies, but TLS/SSL is not used by every hosted application since the data being displayed does not require the encryption of the ... |
| V-214302 | Medium | Cookies exchanged between the Apache web server and the client, such as session cookies, must have cookie properties set to prohibit client-side scripts from reading the cookie data. | A cookie can be read by client-side scripts easily if cookie properties are not set properly. By allowing cookies to be read by the client-side scripts, information such as session identifiers ... |
| V-214301 | Medium | The Apache web server cookies, such as session cookies, sent to the client using SSL/TLS must not be compressed. | A cookie is used when a web server needs to share data with the client's browser. The data is often used to remember the client when the client returns to the hosted application at a later date. A ... |
| V-214300 | Medium | The Apache web server must only accept client certificates issued by DoD PKI or DoD-approved PKI Certification Authorities (CAs). | Non-DoD approved PKIs have not been evaluated to ensure that they have security controls and identity vetting procedures in place that are sufficient for DoD systems to rely on the identity ... |
| V-214295 | Medium | The Apache web server must set an absolute timeout for sessions. | Leaving sessions open indefinitely is a major security risk. An attacker can easily use an already authenticated session to access the hosted application as the previously authenticated user. By ... |
| V-214294 | Medium | Debugging and trace information used to diagnose the Apache web server must be disabled. | Information needed by an attacker to begin looking for possible vulnerabilities in a web server includes any information about the Apache web server and plug-ins or modules being used. When ... |
| V-214297 | Medium | The Apache web server must restrict inbound connections from nonsecure zones. | Remote access to the Apache web server is any access that communicates through an external, non-organization-controlled network. Remote access can be used to access hosted applications or to ... |
| V-214296 | Medium | The Apache web server must set an inactive timeout for sessions. | Leaving sessions open indefinitely is a major security risk. An attacker can easily use an already authenticated session to access the hosted application as the previously authenticated user. By ... |
| V-214291 | Medium | The Apache web server must be tuned to handle the operational requirements of the hosted application. | A denial of service (DoS) can occur when the Apache web server is so overwhelmed that it can no longer respond to additional requests. A web server not properly tuned may become overwhelmed and ... |
| V-214290 | Medium | The Apache web server document directory must be in a separate partition from the Apache web servers system files. | A web server is used to deliver content on the request of a client. The content delivered to a client must be controlled, allowing only hosted application files to be accessed and delivered. To ... |
| V-214293 | Medium | Warning and error messages displayed to clients must be modified to minimize the identity of the Apache web server, patches, loaded modules, and directory paths. | Information needed by an attacker to begin looking for possible vulnerabilities in an Apache web server includes any information about the Apache web server, backend systems being accessed, and ... |
| V-214292 | Medium | The Apache web server must display a default hosted application web page, not a directory listing, when a requested web page cannot be found. | The goal is to completely control the web user's experience in navigating any portion of the web document root directories. Ensuring all web content directories have at least the equivalent of an ... |
| V-214299 | Medium | The Apache web server application, libraries, and configuration files must only be accessible to privileged users. | The Apache web server can be modified through parameter modification, patch installation, upgrades to the Apache web server or modules, and security parameter changes. With each of these changes, ... |
| V-214298 | Medium | Non-privileged accounts on the hosting system must only access Apache web server security-relevant information and functions through a distinct administrative account. | By separating Apache web server security functions from non-privileged users, roles can be developed that can then be used to administer the Apache web server. Forcing users to change from a ... |
| V-214279 | Medium | The Apache web server must produce log records containing sufficient information to establish what type of events occurred. | Apache web server logging capability is critical for accurate forensic analysis. Without sufficient and accurate information, a correct replay of the events cannot be determined. Ascertaining ... |
| V-214278 | Medium | The Apache web server must use encryption strength in accordance with the categorization of data hosted by the Apache web server when remote connections are provided. | The Apache web server has several remote communications channels. Examples are user requests via http/https, communication to a backend database, and communication to authenticate users. The ... |
| V-214277 | Medium | The Apache web server must perform server-side session management. | Session management is the practice of protecting the bulk of the user authorization and identity information. This data can be stored on the client system or on the server. When the session ... |
| V-214304 | Low | The Apache web server must be configured in accordance with the security configuration settings based on DoD security configuration or implementation guidance, including STIGs, NSA configuration guides, CTOs, and DTMs. | Configuring the Apache web server to implement organization-wide security implementation guides and security checklists guarantees compliance with federal standards and establishes a common ... |
Apache HTTP Server, free download. Apache HTTP Server 2.4.43: The Apache HTTP Server Project is an effort to develop and maintain an open-source HTTP server for modern operating systems including UNIX and Windows NT.
Step 1
If you do not already have it, download the Visual C++ Redistributable for Visual Studio 2012 and install it. You can check if you already have it by going to the Programs and Features control panel, and looking for 'Microsoft Visual C++ 2012 Redistributable'. This Microsoft software package contains dependencies for the Windows version of Apache server.
Step 2
Download the latest Apache server (httpd) from Apache Lounge. If you are not sure if you need the Win64 or Win32 version, click on your Start Menu, right-click on Computer, and click Properties. Under System Type, it will tell you if you have a 32-bit or 64-bit system.
You might wonder why you are downloading from Apache Lounge and not the official Apache site. Apache Lounge distributes Windows versions of the latest Apache build. You can download from the official Apache site, but will then need to compile your own build, which is well beyond the scope of this guide.
At the time of writing, the latest version of Apache server (httpd) available at Apache Lounge is 2.4.7, so that version will be referenced in this guide. If you have a newer version, you should be able to simply substitute it, unless major changes have been made.
Step 3
You should now have a zip file named httpd-2.4.7-win32-VC11.zip or similar in your download folder. Extract the Apache24 folder it contains to your desired location for your server to run. I simply put it in the Program Files folder, so my path to it looks like:
C:/Program Files/Apache24From this point on I'll assume you have your Apache server in the same folder. If not, adjust accordingly.
Step 4
Now to configure your server. Inside the Apache24 folder is a conf folder, with a file called httpd.conf. That is the main configuration file. Open it in a text editor as you'll need to make a handful of edits:
ServerRoot
Find the line that starts with ServerRoot (approximately line 37). Change it to:
Apache Web Server 2.4 Free
ServerRoot 'C:/Program Files/Apache24'ServerName
Find the line that contains ServerName (approximately line 217). Remove the pound sign (#) that precedes it. Then change it to:
ServerName localhost:80This will mean that you access your web server by typing localhost into your browser (http://localhost/).
DocumentRoot
The document root is where Apache looks for your website files. Find the line that starts with DocumentRoot (approximately line 241). Change it to reflect the position of your document root, which should be:
DocumentRoot 'C:/Program Files/Apache24/htdocs'Then change the line directly below it to match the new position:
<Directory 'C:/Program Files/Apache24/htdocs'>DirectoryIndex
Scroll down to the line that has DirectoryIndex index.html (approximately line 275). Add index.php in there or any other files you need your server to recognize as index files. For example:
DirectoryIndex index.php index.htmlStep 5
Navigate to the following folder:
C:/Windows/System32/drivers/etcOpen the hosts file with a text editor and add the following line before everything (on its own line):
127.0.0.1 localhostThis tells windows that when you try to navigate to localhost in a browser, it should direct the requests to your own computer (which your server now resides on). Learn more about the hosts file here.
Step 6
Your server is now configured and should be functional. Start it by opening the following file:
C:/Program Files/Apache24/bin/httpd.exe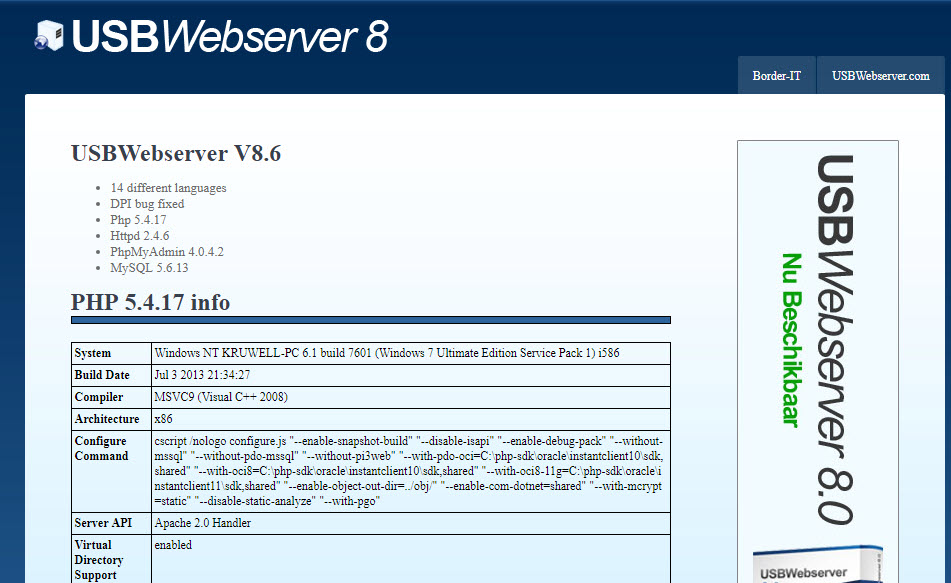
It should be a blank black window. This is good, meaning there were no error messages. Keep it minimized while you want your server to be running. You can stop your server by closing the window.
With your server running, you can use localhost (type it into your browser, like: http://localhost/) to access your web files. Your server uses the web files in your htdocs folder, which is here:
C:/Program Files/Apache24/htdocsThere will already be a simple HTML file in there.
Additional Configuration
Apache Web Server Versions
You my want to move your document root somewhere other than the default htdocs folder. To do this, open the httpd.conf file again and change the location for the DocumentRoot and the following line (approximately lines 241 and 242).
Server Apache
I use wwwroot for my document root because I originally started on IIS. So my document root is at:
C:/wwwrootYou can have it anywhere you want.
mod_rewrite
Apache Web Server 2.4.18
If you want to enable mod_rewrite on your Apache server, search for the line that contains mod_rewrite.so (in httpd.conf) and remove the preceding pound sign (#).
Apache Web Server Download
One last thing. Any changes you make to the httpd.conf file will require a restart of the web server (close it and open it again) to take effect.